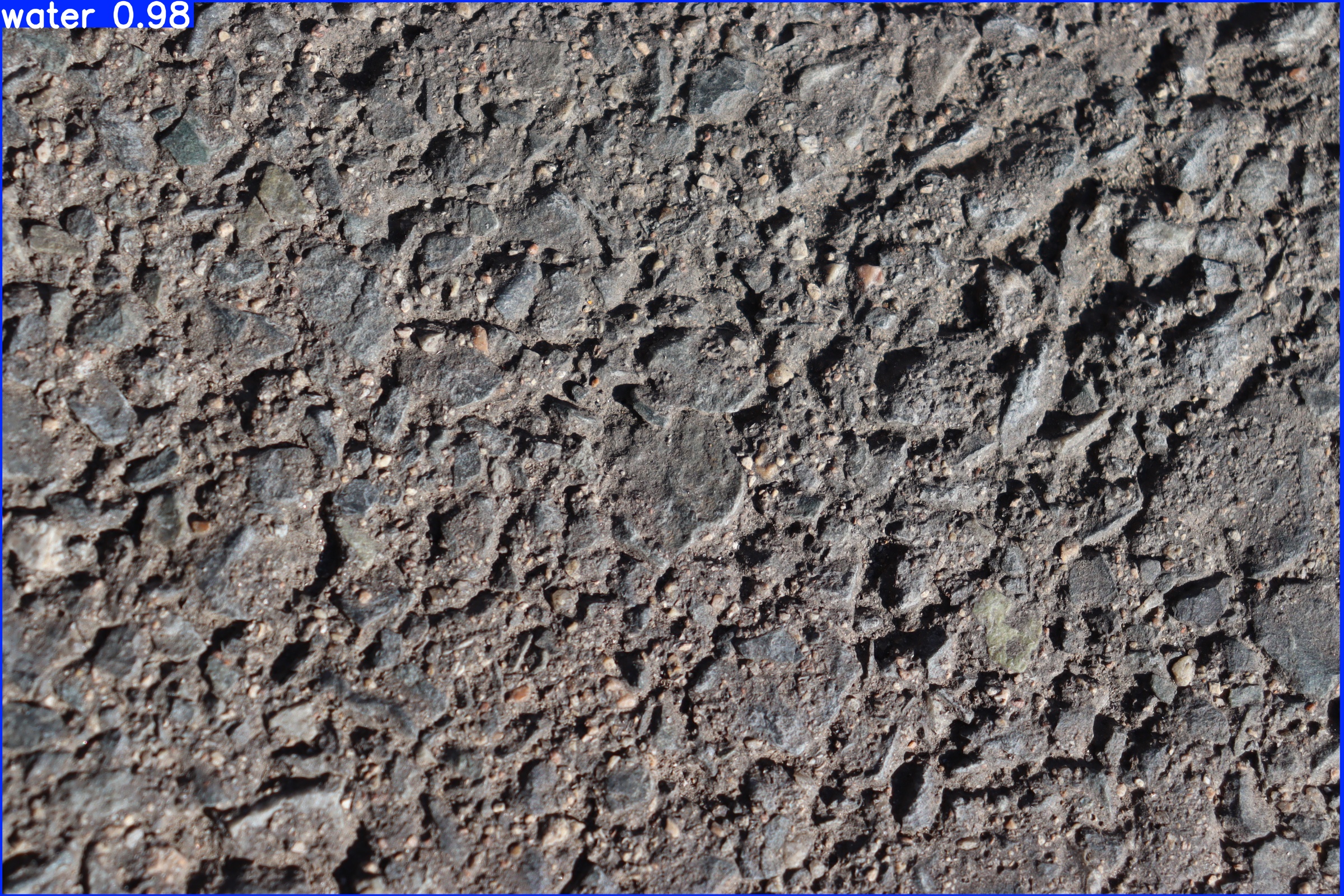
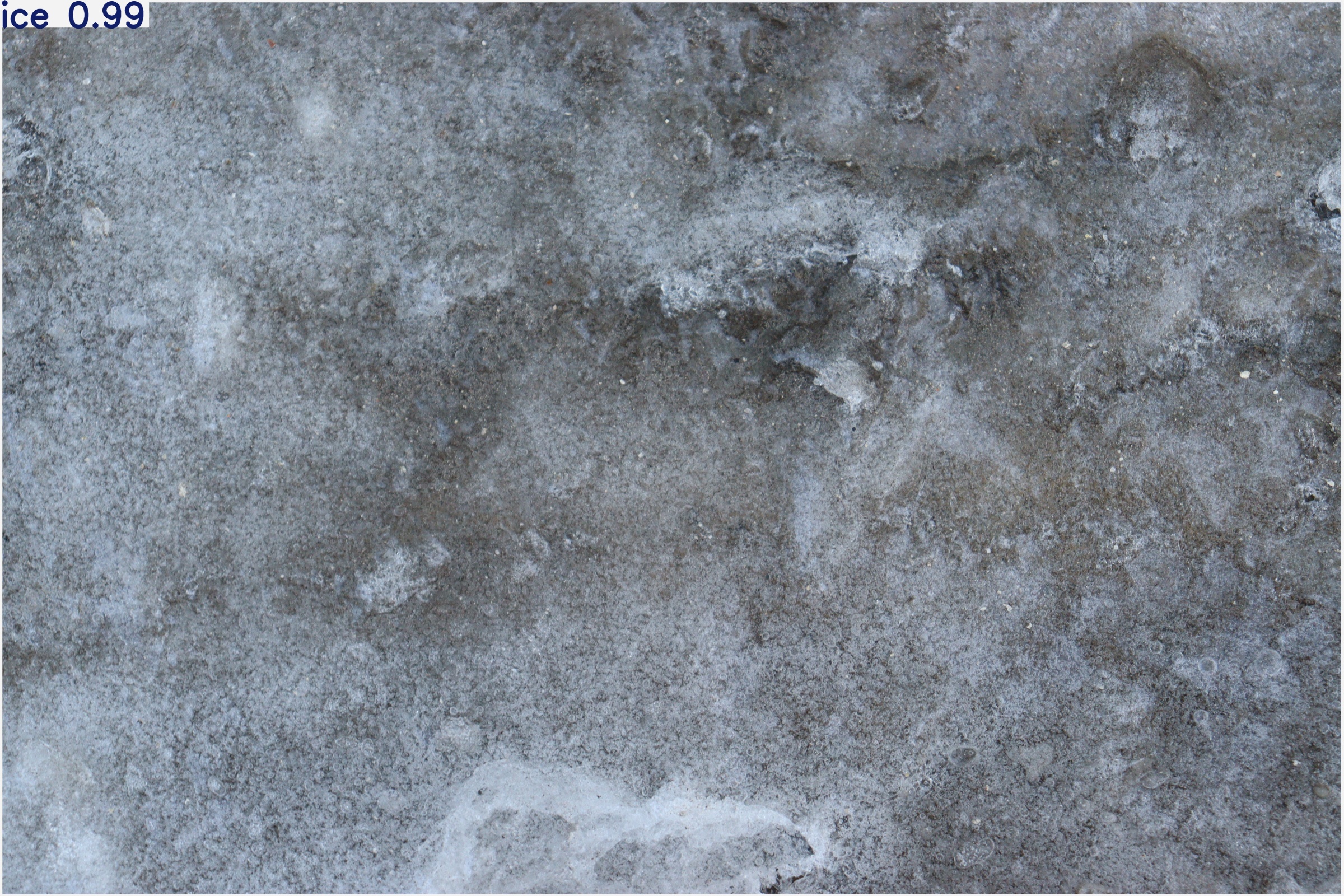
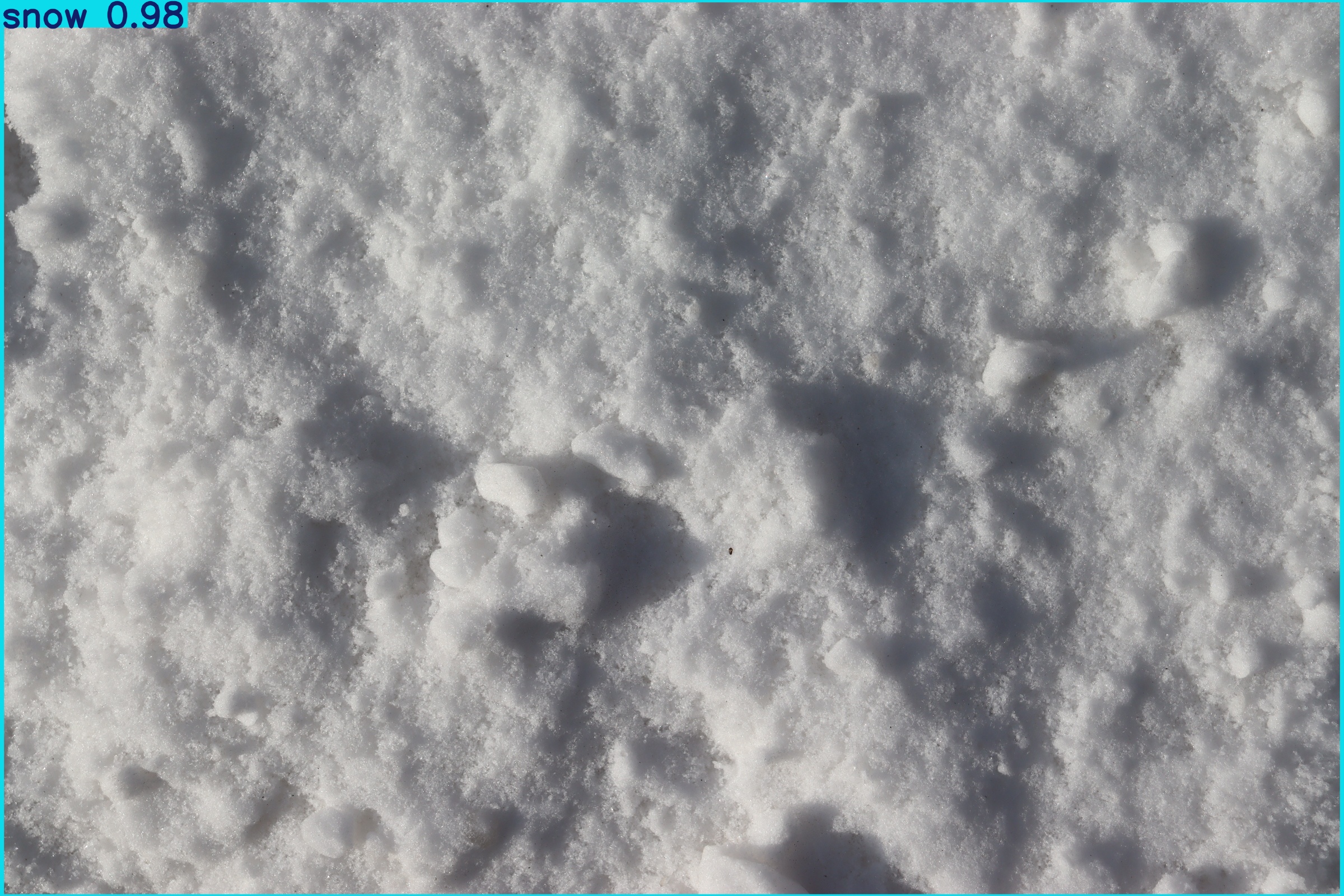
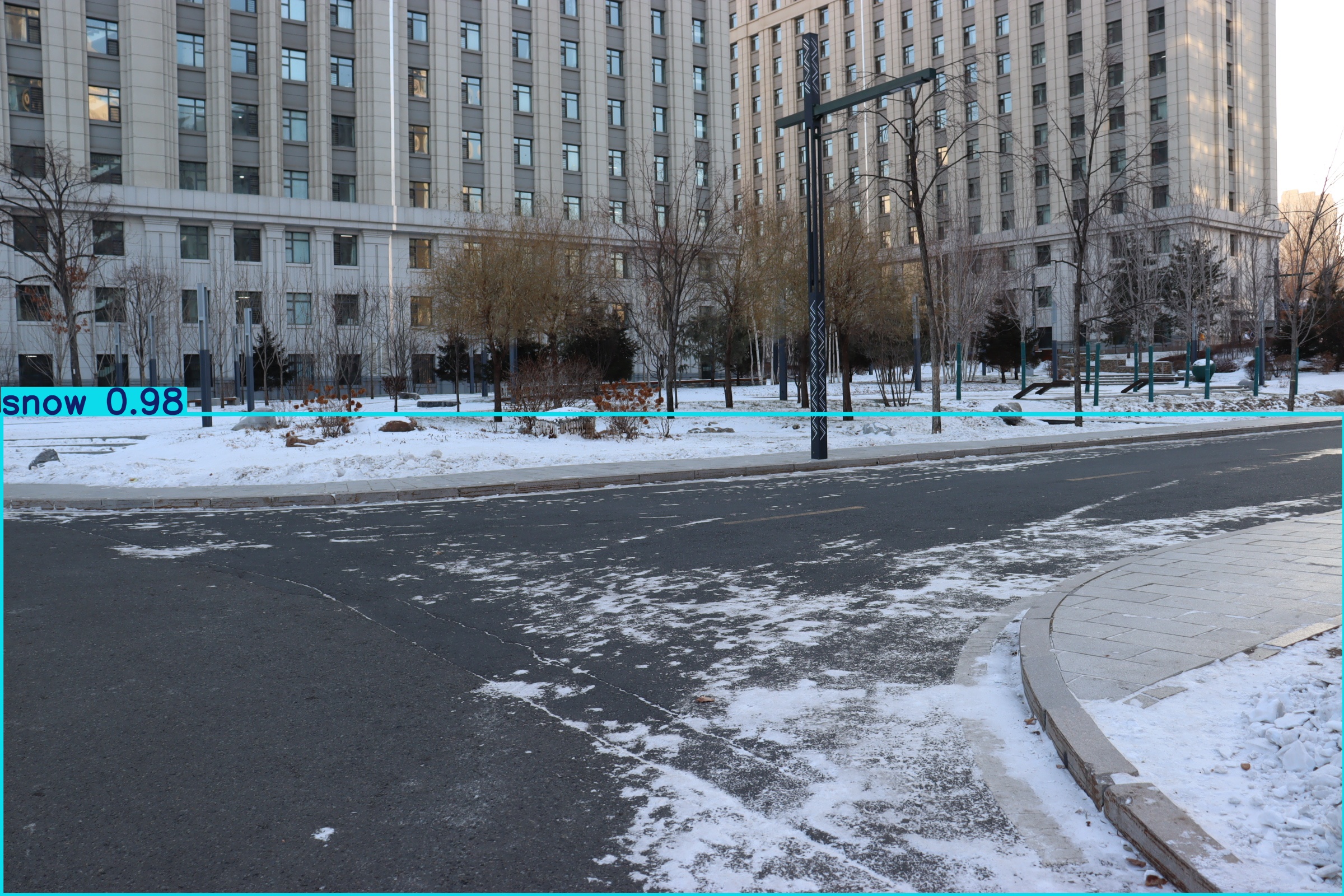
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
| from shapely.geometry import box
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as np
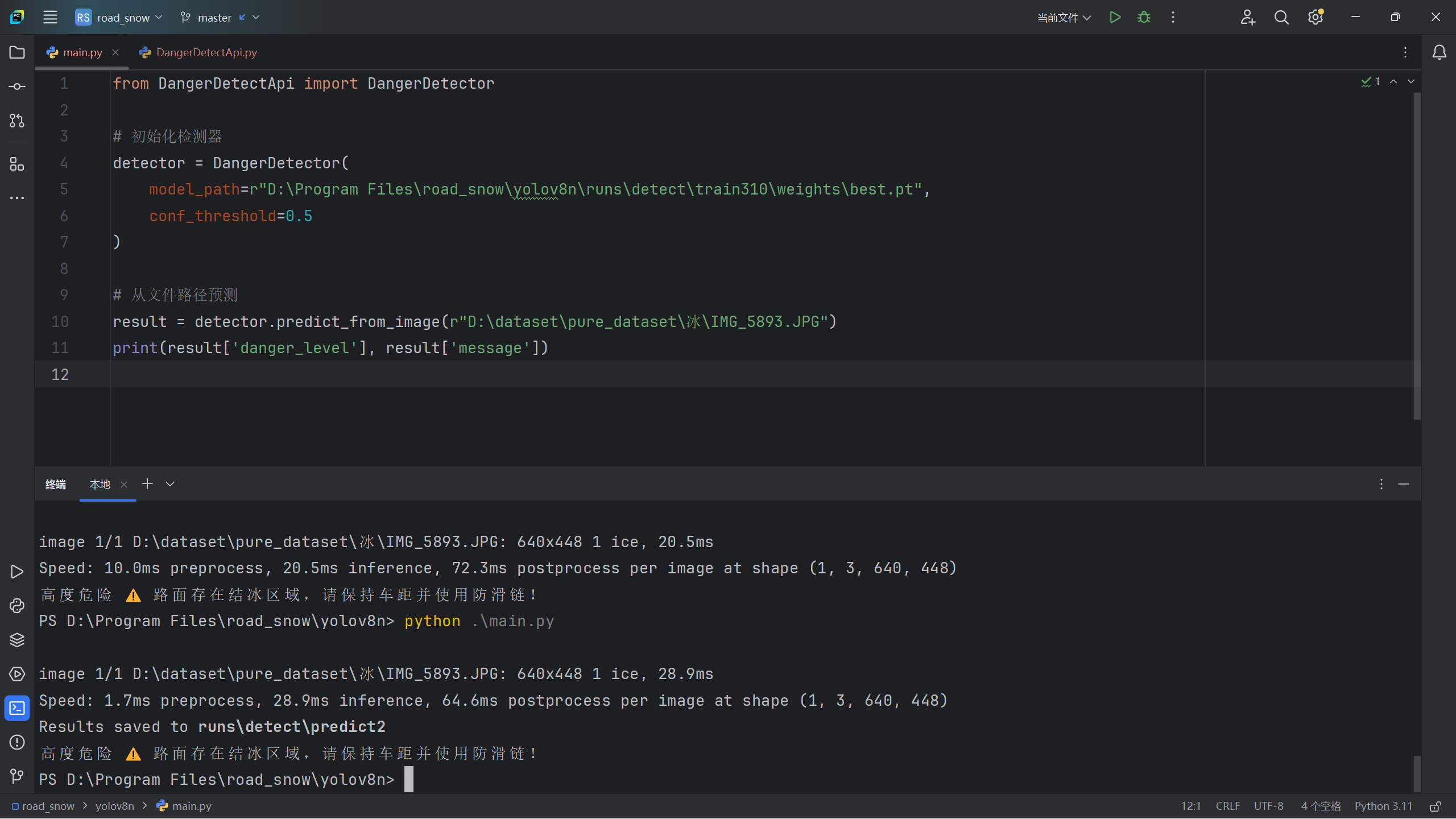
class DangerDetector:
"""路面危险评估API核心类(精确面积计算版)"""
def __init__(self, model_path: str, conf_threshold: float = 0.5):
self.model = YOLO(model_path)
self.conf_threshold = conf_threshold
self.class_map = {0: "snow", 1: "ice"}
self.priority = {"ice": 3, "snow": 2, "water": 1}
self.messages = {
"ice": "⚠️ 路面存在结冰区域,请保持车距并使用防滑链!",
"snow": "❄️ 路面存在积雪,请保持车距!",
"water": "💧 路面湿滑,建议减速慢行!",
"safe": "✅ 路面状况安全,可正常行驶"
}
def _calculate_danger_level(self, results, image_width: int, image_height: int) -> Tuple[str, str]:
"""优化后的危险评估算法"""
detections = []
if results.boxes:
boxes = results.boxes.cpu().numpy()
for i in range(len(boxes.xyxy)):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes.xyxy[i]
conf = boxes.conf[i]
cls_id = int(boxes.cls[i])
area = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
detections.append({
"class": self.class_map[cls_id],
"coords": (x1, y1, x2, y2),
"confidence": conf,
"area": area
})
sorted_detections = sorted(
detections,
key=lambda x: (
-self.priority.get(x["class"], 0),
-x["area"],
-x["confidence"]
)
)
covered_areas = []
ice_area = snow_area = water_area = 0
for detection in sorted_detections:
cls = detection["class"]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = detection["coords"]
current_box = box(x1, y1, x2, y2)
current_polygon = current_box
valid_area = current_polygon
for existing in covered_areas:
if valid_area.intersects(existing["geometry"]):
valid_area = valid_area.difference(existing["geometry"])
effective_area = valid_area.area
if effective_area > 0:
for existing in covered_areas:
if current_polygon.intersects(existing["geometry"]):
overlap = existing["geometry"].intersection(current_polygon)
if overlap.area > 0:
if existing["class"] == "ice":
ice_area -= overlap.area
elif existing["class"] == "snow":
snow_area -= overlap.area
elif existing["class"] == "water":
water_area -= overlap.area
if cls == "ice":
ice_area += effective_area
elif cls == "snow":
snow_area += effective_area
elif cls == "water":
water_area += effective_area
new_geometry = current_polygon
for existing in covered_areas:
if new_geometry.intersects(existing["geometry"]):
new_geometry = new_geometry.union(existing["geometry"])
covered_areas.append({
"class": cls,
"geometry": new_geometry,
"confidence": detection["confidence"]
})
total_pixels = image_width * image_height
weighted_ice = ice_area
weighted_snow = snow_area
weighted_water = water_area
danger_value = (weighted_ice + weighted_snow + weighted_water) / total_pixels
thresholds = {
"high": 0.7 ,
"medium": 0.4 ,
"low": 0.2
}
if danger_value >= thresholds["high"]:
danger_level = "高度危险"
elif danger_value >= thresholds["medium"]:
danger_level = "中度危险"
elif danger_value >= thresholds["low"]:
danger_level = "轻度危险"
else:
danger_level = "安全"
dominant_class = max(
["ice", "snow", "water"],
key=lambda x: (ice_area, snow_area, water_area)[["ice", "snow", "water"].index(x)]
)
message = self.messages[dominant_class] if danger_level != "安全" else self.messages["safe"]
return danger_level, message
def predict_from_image(self, image_path: str) -> dict:
"""
从图片文件路径进行预测
:param image_path: 图片文件路径
:return: 包含危险等级和提示信息的字典
"""
results = self.model.predict(
source=image_path,
save=True,
conf=self.conf_threshold
)
img = results[0].orig_img
h, w = img.shape[:2]
danger_level, message = self._calculate_danger_level(results[0], w, h)
return {
"danger_level": danger_level,
"message": message,
"image_size": (w, h),
"results": results
}
def predict_from_array(self, image_array : np.ndarray) -> dict:
"""
从numpy数组进行预测
:param image_array: 输入图像数组 (HWC格式)
:return: 包含危险等级和提示信息的字典
"""
results = self.model.predict(
source=image_array,
save=False,
conf=self.conf_threshold
)
h, w = image_array.shape[:2]
danger_level, message = self._calculate_danger_level(results[0], w, h)
return {
"danger_level": danger_level,
"message": message,
"image_size": (w, h),
"results": results
}
|